Building a Front-End Online Presence
A Technical Exploration
Introduction
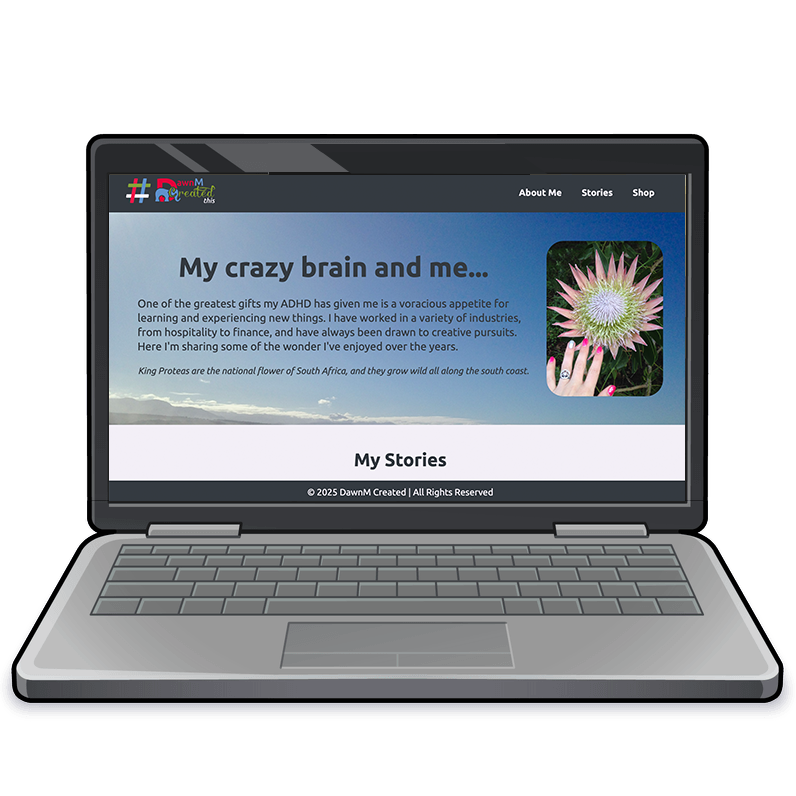
As part of my journey to becoming a front-end web developer, I created this mini portfolio webpage to showcase my stories and skills. This article will take you through the technical aspects of the code used in the webpage, highlighting key concepts I'd learned so far.
HTML Structure
The backbone of this webpage is its HTML structure, which is semantic and well-organized. Here's a breakdown of the key sections:
-
<header>: Contains the page title and navigation bar. -
<nav>: Holds the navigation links, including anchor links to other sections of the page. -
<section>: Defines different sections such as the hero section and portfolio, each focusing on specific content. -
<footer>: Includes copyright information and closes the webpage.
CSS Styling
The webpage's layout and style were created using modern CSS techniques:
- Flexbox Layout: Flexbox is used extensively for building flexible, responsive layouts. The navigation bar and portfolio cards make use of flexbox to ensure proper alignment and distribution of content.
- Responsive Design: The webpage uses media queries to adjust the layout for different screen sizes, ensuring it looks good on both large and small devices. For example, the hero section changes layout for mobile screens, with an image and text stacked vertically.
-
Background Images and Object Fit: The hero section
employs a background image that adapts to different screen sizes
using
background-size: cover;. For the images in the portfolio section, theobject-fit: cover;property ensures they fill the container without distorting their aspect ratio.
JavaScript for Interaction
Though the webpage initially had no JavaScript, I added a small function to toggle the visibility of the mobile navigation menu:
function toggleMenu() {
const menu = document.getElementById("menu");
menu.classList.toggle("active");
menu.setAttribute("aria-expanded", menu.classList.contains("active"));
}
This script allows users to open and close the navigation menu by clicking the hamburger icon, and updates the aria-expanded attribute for accessibility.
Lessons Learned
Throughout this project, I learned several important concepts and practices for building modern websites:
- Accessibility: Using aria-expanded to make interactive elements accessible to screen readers.
- Mobile-First Design: Prioritizing mobile design first and adapting it for larger screens using media queries.
- Responsive Images: Using techniques like object-fit to ensure images look good across all screen sizes.
- Flexibility: Understanding how flexbox works to create layouts that can adjust depending on the content and screen size.
- HTML Semantics: Structuring the HTML in a clear, meaningful way to improve the page's accessibility and SEO.
Conclusion
This webpage is a portfolio of the stories and experiences that have shaped me, not just a showcase of technical work. By using a combination of HTML, CSS, and a little JavaScript, I've created a webpage that is functional, accessible, and mobile-friendly. I'm excited to continue building on my front-end development skills and creating more engaging, content-driven projects in the future!